INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY
MAIN BRANCHES OF BIOLOGY
OTHER BRANCHES OF BIOLOGY
IMPORTANCE OF STUDYING BIOLOGY
Biology in relation to other Scientific fields.
Forestry: learning about the development and caring and management of different plants( forests) and their products. Biology research has come up with variety of trees as planted to replace that have been cut down.Afforestation trees are grow well to reclaim dry land for human settlement..Reafforestation helps to preserve water catchment so that we can continuous supply of water
SCIENTIFIC PROCESSES IN BIOLOGY
4.Time is how the continuous of experience of events pass to future through the present to the past.The SI unit of time is seconds(s).it measured using Watch or clock
1. Identifying the problems. This is making puzzling observation. or putting question
2. Asking questions.The scientific question will probably require answer or explanation. After gathering evidence.
3. Formulating a hypothesis. It is intelligent guess that tries to explain an observation.
4. Experimentation.is attest that is carried out under controlled condition to determine whether the hypothesis is correct or not
5. Observation and recording data. The scientists observe what happens from the time the experiment is set up to the time it ends
6.Data interpretation. The scientist analyzes the observation and data recorded
7. Conclusion. is the statement that summarizes what a scientists has learnt from an experiment,
BIOLOGY LABORATORY
Specimen: Are collected organisms or part of organisms, e.g. grasshopper, fish, snakes, plants, gills of fish, blood sample, and urine. (A specimen can be freshly picked or preserved).
Models: Are man made structures like body organs, e.g. heart, liver, lungs, skeleton, kidneys human body, eye, ear.
BIOLOGY APPARATUS
2 Sweep nets- Is used for catching small flyin organism such as butterflies and grasshoppers
3.Revolving nose piece – Holds objective lenses in place. Position of the objective
lenses can be changed by manipulating the revolving nose piece.
This type of microscope uses a beam of electrons rather than a beam of light to produce magnified images. Electron wave lengths are much shorter than those of visible light. As a result electron microscopes can resolve much finer detail than light microscope can do
3.Sterilized cotton wool used for cleaning the skin or the wound.
4.Sterilized gauze used to cover wound and prevent it from dirt but also allow enough air.
5.Splints used to support broken bones and is tied using bandages.
6.Elastic bandages used on injured joints or dislocation.
7.Plaster band used to stick on the skin to protect a wound from dirt. It also minimizes bleeding.
8.Safety pins used for holding pieces of bandages or cloth together.
9.Methylated spirit used for cleaning wounds and surgical instruments like tongs, tweezers, and scissors.
10. Liniment can be used to reduce muscle pains.
11.Iodine solution used on fresh wounds.
12.Gentian Violet solution (GV) applied on wounds
13. like, Antibiotic solution for killing microorganism like bacteria.
14. Pain killers like panadol and aspirin used to reduce pain.
15.Pair of tongs used for picking up and holding things when cleaning wounds.
16. Clinical thermometer for measuring temperature of a sick person.
17.Jar of petroleum jelly for applying on cuts, scrapes, bruises and small wounds.
18.Soap used for cleaning wound and hands during first aid.
19. Water
1.. SNAKE BITE
TREATMENT OF SNAKE BITE
i.Calm the person and have them lie or sit down
2. INSECT BITES AND STING
TREATMENT
i.Remove the sting by scrapping gently using a blunt object such as plastic card.
-Do not use your fingers or sharp object because this will make the sting to release more venom into the body
ii.Wash the stung area with soap and water
iii. Apply baking soda paste on the stung area(use ratio of 1 teaspoon of water to 3 teaspoon)The sting is acidic, baking soda is a base and so it neutralize the aid
iv.Apply a cold compression on the affected area to relieve pain and swelling.
-If the victim develops allergic reactions for example nausea,diarrhea, dizziness or swelling of the lips or throat take the person to the hospital immediately
3. EXCESSIVE BLEEDING FROM WOUND.
4. NOSE BLEEDING.
5.ELECTRIC SHOCK.
7.VOMITING
TREATMENT.
9.MUSCLE CRAMPS.
- Deep and dirty wound.
17. EMERGENCY CAUSED BY HEAT..
Biology is the
scientific study of living organism and life.
Today the scope
of biology encompasses living things and their interaction with non-living
things in their physical environment
Biology comes from two Greek words . Bios= life . Logos= study or knowledge.
Biology comes from two Greek words . Bios= life . Logos= study or knowledge.
MAIN BRANCHES OF BIOLOGY
When we think
of living things, often we think of animals and plants. These
two main branches of biology, namely:
i. Zoology: scientific study of animals
.ii. Botany: scientific study of plants. However, in the world of living organisms there are other organisms which are neither plants nor animals; example: bacteria, fungi, protoctista and viruses. Since biology is more than animals and plants, we have other branches of biology
i. Zoology: scientific study of animals
.ii. Botany: scientific study of plants. However, in the world of living organisms there are other organisms which are neither plants nor animals; example: bacteria, fungi, protoctista and viruses. Since biology is more than animals and plants, we have other branches of biology
OTHER BRANCHES OF BIOLOGY
Bacteriology is the scientific study of bacteria.
Mycology is the scientific
study of fungi.
Microbiology is the scientific
study of micro-organisms.
Cytology is the scientific
study of the structure and function of cells.
Genetics is the study of
inheritance and variations in inheritance.
Entomology is the study of insects.
Virology is the scientific
study of virus.
Taxonomy is the scientific study of
classification.
Anatomy is the scientific study
of structure of organisms.
Protozoology is the scientific study
of protozoa.
Physiology is the study of how
the bodies of organisms and their various parts functions.
BASIC BIOLOGICAL CONCEPTS
Life, is the state of being alive or existing. That is the ability to
grow and reproduce. All living things are composed of one or more cells.Cell,
is the basic unit of life. A cell is composed of nucleus, cytoplasm and cell
membrane.Organism (Living things). Is an individual living system, such as
animal, plant or micro-organisms(bacteria)that is capable of reproduction,
growth and maintenance of worn out tissues.Non living thing is anything that
does not exist or is dead.
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS
i. Nutrition(Feeding). All living things take in and
assimilate materials (food) for growth, maintenance and repair of worn out
tissues.)
ii. Movement and locomotion: Movement is the act of changing position or posture. It can involve the whole body or part e.g. plants move by growing: roots towards source of water; stem towards light.Locomotion: is the movement of the whole body: change in position.
ii. Movement and locomotion: Movement is the act of changing position or posture. It can involve the whole body or part e.g. plants move by growing: roots towards source of water; stem towards light.Locomotion: is the movement of the whole body: change in position.
iii.Growth
and development:-Growth: Irreversible increase in size and
mass.Development: irreversible change in the complexity and structure of living
things:(e.g. ability to reproduce when you reach puberty or ability to speak.)
iv.Reproduction: is
the ability to give rise to the new individual of the same kind(species).
v. Sensitivity
or Irritability (response).Sensitivity: ability to detect changes in
the surroundings using sense organs in animals( eyes, skin, ears, nose, tongue)
and hormones in plants.Irritability (response): ability to react to changes in
the immediate environment e.g. temperature, humidity, light, pressure and
chemicals.
vi. Respiration: is
the process by which food substances are chemically broken down in all living
cells to release energy, carbon dioxide and water. The energy is used
for:
vii. Gaseous
exchange: process whereby respiratory gases(oxygen and carbon dioxide)
are passed across the respiratory surfaces.
viii.
Excretion: process by which excess waste and harmful materials
resulting from body metabolisms are eliminated from the body.
ix. Death:
is the end of life also it is the point at which processes and organs that
maintain an organism no longer function, e.g. permanent cessation of heart beat
in human.
IMPORTANCE OF STUDYING BIOLOGY
1. To
understand one self better, as we are part of the living world.
2. It helps us
to understand our environment better. Hence solve environmental problems e.g.
shortage of food, poor health services, misuse of environmental resources
(forests, water, soil, wildlife).
3. Helps us to
appreciate nature. we learn many fascinating things aabout different organisms
and how they function.
4. To enter
into carrier e.g. medicine, agriculture, biotechnology, public health, genetic
engineering.
5. To know
causative agents, symptoms, transmission, prevention of infectious diseases and
their treatment.
6. Living
organisms provide us with basic needs e.g. food, clothing & shelter.
7. Answers for
fundamental questions: when did life begin?
8. To acquire
scientific skills e.g. planning, observing, experimenting, classifying,
measuring, analyzing data, evaluation & conclusion which are very useful in
daily life.
9 Biology
studies identify and group living things
Biology in relation to other Scientific fields.
Biology is related to many other field of study agriculture, medicine, harmacy,
foresty
1.Agriculture: is the practice of growing crops and rearing
animals for food and for money. Biology research finding on crops and livestock
have led to improve agricultural production. For example a
selected organisms like plants and animals for domestic purposes
yield more products.
Medicine and Pharmancy: medicine is the study of prevention, treatment and cure
diseases and pharmancy deals with the preparation and administration of
medicine. by studying anatomy and physiology we discover drugs (medicine) from
other organisms i.e.: plants-herbs, antibiotics. Study of microorganisms help
to understand causes, vaccine and prevention of many diseases.
Nutrition: as biology study anatomy and physiology it helps us to know what
composition and value of different type of balanced diet required for different
age groups.
Forestry: learning about the development and caring and management of different plants( forests) and their products. Biology research has come up with variety of trees as planted to replace that have been cut down.Afforestation trees are grow well to reclaim dry land for human settlement..Reafforestation helps to preserve water catchment so that we can continuous supply of water
SCIENTIFIC PROCESSES IN BIOLOGY
Biology needs
scientific methods of research and investigation. This can be done either by
field observation (out doors) or laboratory experimentation (indoors).
These skills
include .i Observation. ii.measurement. ii.Experiment
Observation is
the study of keenly. We can study living things in many ways Example use sense
of organ.
Measurement. Scientists use specific instruments and units of measurements in
their investigation.
1.Mass s is the quantity of matter in objects.The SI unit is Kilogram (Kg).It measured by using Weighing scales
2.Length is the measurement of the distance or dimension from one point to another the SI UNIT IS metre (m).It measured using a ruler of tape measure
.
1.Mass s is the quantity of matter in objects.The SI unit is Kilogram (Kg).It measured by using Weighing scales
 |
| Fig. Beam balance |
2.Length is the measurement of the distance or dimension from one point to another the SI UNIT IS metre (m).It measured using a ruler of tape measure
.
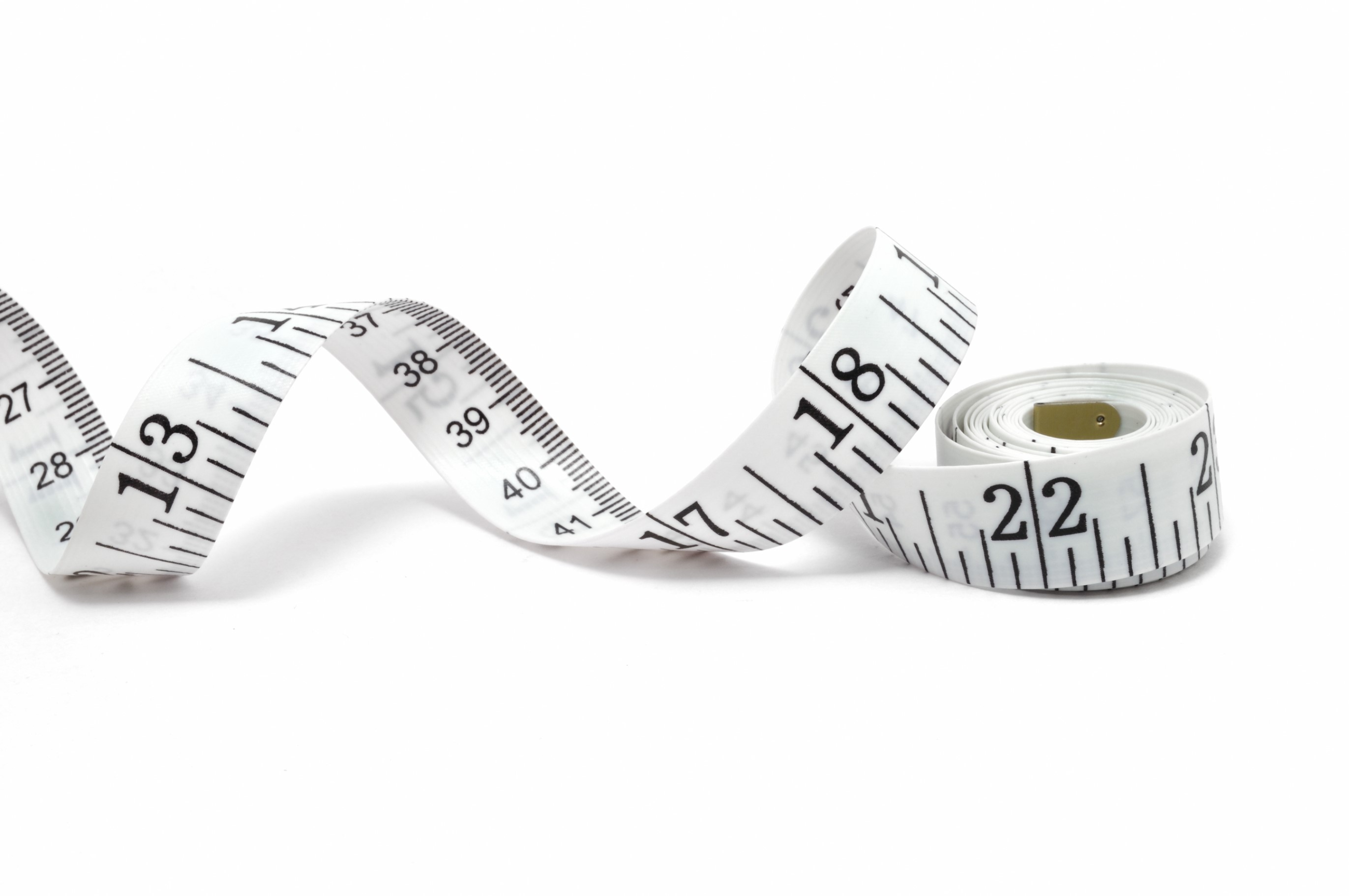 |
| Fig Tape measure |
3.Temperature is measure how hot or
cold a substances is. The SI unit is Kelvin(K), degree Celsius(oC)or
Fahrenheit(oF).It measured using thermometer
 |
| Fig Thermometer |
4.Time is how the continuous of experience of events pass to future through the present to the past.The SI unit of time is seconds(s).it measured using Watch or clock
| Fig.Stop watch |
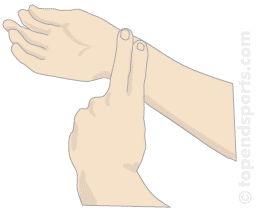
5.Pulse
rate refers to average beating of your heart. You can find how fast
your heart is beating, that is your heart rate, by feeling your pulse.
How to measure your pulse rate
- Sit down comfortably on a chair with the palm of your hand facing upwards.
- Gently place the index and middle fingers of your other hand on your wrist (see the diagram below). Can you feel your pulse as a repeated throb?
- If necessary change the position of your finger until you can feel your pulse rate well. Count the number of heart beats in one minute.
- Repeat step 3 four times.
- Write down the number of beats per minute.
- Work out the average. This is what is called average heart rate per minute. It tells you how fast your heat is beating.
Measuring the pulse rate

THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD
The scientific
method is a way of studying thing by testing facts systematically. it
follows the steps explained below
1. Identifying the problems. This is making puzzling observation. or putting question
2. Asking questions.The scientific question will probably require answer or explanation. After gathering evidence.
3. Formulating a hypothesis. It is intelligent guess that tries to explain an observation.
4. Experimentation.is attest that is carried out under controlled condition to determine whether the hypothesis is correct or not
5. Observation and recording data. The scientists observe what happens from the time the experiment is set up to the time it ends
6.Data interpretation. The scientist analyzes the observation and data recorded
7. Conclusion. is the statement that summarizes what a scientists has learnt from an experiment,
SIMPLE BIOLOGY EXPERIMENTS
Biological
experiments can be done to study different features of living things.
BIOLOGY LABORATORY
Laboratory is a
special room that is specially designed for carry out the scientific experiment.A
biology laboratory is place or room where biological experiment are
conducted.
 |
| Fig.Biology laboratory |
UNIQUE FEATURES OF GOOD LABORATORY
i. adequate
space .is important to allow students to carry out experiments and
facilitate free movement around laboratory hence reduce chance of occurrence of
an accident.
ii.Proper
lighting. This help students to see instruction,warning sign,
safety, symbols label on reagent bottle and procedure of experiment properly.
iii.Good ventilation.It
help circulation of air,removal of fumes and gases and prevent suffocation,and
prevent the laboratory users from short-term exposure to toxic substances.
iv.A
source of water.Water is used as solvent, for boiling mounting
specimens, washing and cleaningv.Source of heating Source of
heating is needed for heating during experiment.
vi.Adequate
storage, For storing apparatus and specimens
CARING FOR LABORATORY SPECIMENS
Biological
studies often involve keeping live specimens like plants, fish, insects and
small mammals.
-The alive
specimens should be properly looked after and have the correct food, water and
surroundings.
-If they are
wild, they must be returned to their respective environment after
observation.
Laboratory Rules or safety regulations
i. Don’t enter
the laboratory without teachers’ permission.
ii. Never
handle any chemical, specimen or apparatus without teacher’s instruction.Don’t
run in the laboratory
iii. Don’t
throw things in the laboratory
i. Do not eat/drink/taste
anything in the laboratory
v. Listen carefully to the teachers’ instructions.
v. Listen carefully to the teachers’ instructions.
vi. Clean your
bench after any experiment.
vii. Wash your hands after experiment
viii. Report all accidents and breakage to the teacher
ix. Observe the safety labels on the containers and take necessary precautions.Never use broken glass vessels.
x. Never play with gas and water taps in the laboratory.
vii. Wash your hands after experiment
viii. Report all accidents and breakage to the teacher
ix. Observe the safety labels on the containers and take necessary precautions.Never use broken glass vessels.
x. Never play with gas and water taps in the laboratory.
xi. Wash all
apparatus before and after use (always use clean apparatus).
xii. Extinguish
all burners and turn off water tap when you do not need them.Never use
laboratory apparatus for eating or drinking.Keep the laboratory clean and safe.
xiii. Always keep inflammable substances away from flame.
xiii. Always keep inflammable substances away from flame.
BIOLOGY LABORATORY DIFFER
FROM OTHER FACILITIES
-In the Biology
laboratory we can find preserved specimens and models., cages,
charts
| Fig Cage |
-Equipment and
Apparatus for carrying out biological experiments.
-Sinks and
water supply.
-Gas supply and
burners (Bunsen burners and spirit burners)
-Fridge for
storing specimen-Oven for drying specimens or for experiments to culture
bacteria.
-It has large windows
for enough supply of air and light.
-Presence of
aquaria
-Has special
apparatus such as microscope and microscope slides,dissecting kit and hand
lens.
Specimen: Are collected organisms or part of organisms, e.g. grasshopper, fish, snakes, plants, gills of fish, blood sample, and urine. (A specimen can be freshly picked or preserved).
| Fig preserved specimen |
Models: Are man made structures like body organs, e.g. heart, liver, lungs, skeleton, kidneys human body, eye, ear.
BIOLOGY APPARATUS
Biology
apparatus are tools and equipment needed in order to study biology
effectively. This includes
1. Hand lens.- is used to magnify specimens. Magnification enable scientists to observe small organism.
1. Hand lens.- is used to magnify specimens. Magnification enable scientists to observe small organism.
| Hans lens |
| . |
|
2 Sweep nets- Is used for catching small flyin organism such as butterflies and grasshoppers
| Sweep net |
3.Fishing nets.These are used for catching fish and other aquatic animals
4.Pooter-Is deivice that scientists use
to pich up small organisms such as insects,without hurting them
| Add caption |
-It has two
tubes.The scients sucks through one tube and the organism is drawn into the
pooter through the other tubes
5.Quadrat-Is awooden or metallic grid.It is used to estimate the population of organisms in area
6.Specimen bottle.This is a container where specimens are put
7.Petri dish-This is shallow glass or plastic containerwhere spemimens are put for close observation
8.Mortar and pestle.
A mortar is a small hard bowl,
A pestle is a small heavy tool used for crushing things
-Both are usually for crushing or grinding substances
9. Crucible-Is a container in which substance are heated to very high temperature
10.Dissecting kit
their contains of the following.
5.Quadrat-Is awooden or metallic grid.It is used to estimate the population of organisms in area
6.Specimen bottle.This is a container where specimens are put
| Fig specimen bottle |
7.Petri dish-This is shallow glass or plastic containerwhere spemimens are put for close observation
| Petri dish |
8.Mortar and pestle.
A mortar is a small hard bowl,
A pestle is a small heavy tool used for crushing things
-Both are usually for crushing or grinding substances
| Fig mortar and pesstle |
9. Crucible-Is a container in which substance are heated to very high temperature
10.Dissecting kit
their contains of the following.
- dissecting tray
- Forceps for holding the spemen
- Scissors for cutting
- Scalpels for cutting
- A needle for loosening internal parts
- Pins for holding the specimens in place
- Hand lens for close viewing during dissecting
| Open dissecting kit |
11.Thermometer-is used to measure temperature
12.Heat sources-These are used for heating substances in the laboratory Bunsen burner
13.Spatula-is used for scooping powder or crystalline substance

14.Syringes-Are used for transferring small quanties of gases or liquid

15.Watch glasses-is a shallow dish that is used as an evaporating surface or cover for beakers
16.Mounting needle-Is used to lift small delicate specimens

17.Microscope slide and coverslip-
Specimens to be observed on microscope are placed on a slide and covered with a coverslip

THE MICROSCOPE
This is a an instrument that is used in the scientific studies to magnify very small specimens so that their details cab seen
TYPES OF MICROSCOPE
i.Light microscope
ii. Electron microscope
1.The light microscope
This depends on light to illuminate and magnify tiny objects.The lesenses can magnify ibjects up to 2000times

12.Heat sources-These are used for heating substances in the laboratory Bunsen burner
| Fig.Sprit burner |
13.Spatula-is used for scooping powder or crystalline substance
14.Syringes-Are used for transferring small quanties of gases or liquid
15.Watch glasses-is a shallow dish that is used as an evaporating surface or cover for beakers
16.Mounting needle-Is used to lift small delicate specimens
17.Microscope slide and coverslip-
Specimens to be observed on microscope are placed on a slide and covered with a coverslip
THE MICROSCOPE
This is a an instrument that is used in the scientific studies to magnify very small specimens so that their details cab seen
TYPES OF MICROSCOPE
i.Light microscope
ii. Electron microscope
1.The light microscope
This depends on light to illuminate and magnify tiny objects.The lesenses can magnify ibjects up to 2000times
.
| . |
- Eyepiece – Magnify objects under observation since it consists of magnifying lenses.
2.Body tube – Hollow tube attached to the arm. Its function is to hold
eyepiece lens and revolving nose piece.
| . |
4.Coarse adjustment knob – It lowers and raises the body tube so that a clear image
is obtained.
5.Fine adjustment knob – Raises and lowers the body tube to obtain a fine focus.
6. Objective lens – Brings image into focus and magnifies it.
7. Stage – This is a place where specimen to be observed is placed
8.Clips – Hold the slide or specimen in position
9.Mirror – Reflects and directs light to the object under
observation.
10.Diaphragm – Is an aperture that regulates the amount of light passing
through the condenser to illuminate the specimen
11.Condenser – Concentrates light reflected by the mirror.
12.Base or stand – Supports the microscope steadily
13.Arm or limb – Supports the body tube and stage. It is used to hold the
microscope
14.Hinge screw – Raises and lowers the stage.
Magnification
Magnification
power is symbolized by a number and abbreviation X. For example a 10X magnifying
glass magnifies an object by 10 times. An object is magnified by multiplying
the eyepiece lens magnification and objective lens magnification.
Example:
Magnification =
eyepiece lens x objective lens magnification
= 10 × 20= X200
A table of
magnification
Eye
piece lens magnification
|
Objective
lens magnification
|
Total
magnification
|
5
|
20
|
X100
|
10
|
20
|
X200
|
15
|
10
|
X150
|
10
|
25
|
X250
|
20
|
20
|
X400
|
How to use a
microscope
- Turn on your microscope light
- Turn the nose piece so that the small (low power) objective lens clicks into place. Always start with low power lens in place.
- Place the prepared slide on the center of the stage under the clips so that the object is in the center of the opening. Make sure the cover slip is on top
- With your eye at stage level, use the coarse adjustment to bring the object and the low power objective lens as near to each other as possible. The objective lens should not touch the cover slip
- Now with your eye to the eyepiece, slowly move the coarse adjustment to increase the distance between the object and the lens. Continue this until the image is focused.
- Adjust the diaphragm so that the object can be seen as clearly as possible
- To observe the object under medium and high powers, rotate the revolving nose piece to bring the next highest objective lens into position. Make sure you hear the 'click' to ensure that the objective lens is in place. Then, focus using the fine adjustment only.
Ways of handling and carrying a light microscope
- Use both hands to carry the microscope. One hand should hold the base and the other hand should hold the arm.
- Always place the microscope on the desk or table carefully and gently and never place it at the edge of the bench.
- Keep the microscope in an upright position when using liquids or when not in use.
- Keep the stage clean and dry. If any liquids are spilled on the microscope, wipe them up immediately with a piece of tissue.
- Focus with the low-power objective lens first.
- Focus by moving the lens away from the slide, that is, by increasing the working distance.
- Consult your teacher if the lenses are dirty.(viii) Consult your teacher if the adjustments do not work freely.
- When your work is completed, move the low power objective lens into place and remove your slide.
- Keep your microscope covered when it is not in use and keep your work area clean and tidy.
| . |
FIRST AID
First aid is the immediate and temporary care or help administered to an
injured or an ill person before being taken to hospital or before the doctor
comes.Every one should be familiar with the medical components found in the
first aid kit and how to use them, because a very simple intelligent act may
save a person’s life while detailed and ill-informed interference may make
illness or injury worse.
Importance of First Aid
i. Saves life
ii. Reduces pain
iii. Brings hope and encouragement
iv Prevents further accidents, bleeding or injuries.
v. Removes fear of death.
vi. Helps the patient to recover from shock.
FIRST AIDER
First Aid Kit or Box.Is a
small box or bag in which medical components for emergency treatment are put.
It is placed in a safe and accessible place.
FIRST AIDER
The First Aider
is a specialist who gives first aid.
Qualities of the first Aider
- She/he should have
ability to assess the problem and give immediate and appropriate help.
- She/he must be able to
act quickly, quietly, calmly
- She/he should be
sympathetic to the victim
- She/he should be able
to recognize dangerous signs and give immediate help for example detecting
immediately if -breathing has stopped or is failing -there is severe
bleeding-poisoning-fractures
- She/he should be able
to help the injured person without unnecessary movement
Precautions to be observed by the First Aider
The
First Aider should keep himself/herself safe to avoid dangers from the
patient.
Some of the dangers that s/he may face include infection by
pathogens such as viruses and bacteria.So they should:
- Wear protective gloves to avoid contact with blood
- Wear eye protection
- Wear masks and gowns.
COMPONENTS OF THE FIRST AID KIT AND THEIR USE
1.A pair
of scissors, sharp knife, new sterilized razor blades, and needles;
-used for
cutting bandages strings or cutting flaps of skin while cleaning the wound.
2.Assorted bandages. for tying around a part
that has been injured in order to protect or support it.
3.Sterilized cotton wool used for cleaning the skin or the wound.
4.Sterilized gauze used to cover wound and prevent it from dirt but also allow enough air.
5.Splints used to support broken bones and is tied using bandages.
6.Elastic bandages used on injured joints or dislocation.
7.Plaster band used to stick on the skin to protect a wound from dirt. It also minimizes bleeding.
8.Safety pins used for holding pieces of bandages or cloth together.
9.Methylated spirit used for cleaning wounds and surgical instruments like tongs, tweezers, and scissors.
10. Liniment can be used to reduce muscle pains.
11.Iodine solution used on fresh wounds.
12.Gentian Violet solution (GV) applied on wounds
13. like, Antibiotic solution for killing microorganism like bacteria.
14. Pain killers like panadol and aspirin used to reduce pain.
15.Pair of tongs used for picking up and holding things when cleaning wounds.
16. Clinical thermometer for measuring temperature of a sick person.
17.Jar of petroleum jelly for applying on cuts, scrapes, bruises and small wounds.
18.Soap used for cleaning wound and hands during first aid.
19. Water
used for
taking painkillers, cleaning wounds and also for washing hands during first
aid.
WARNING SIGNS
Warning signs on laboratory chemicals and apparatus


7.Risk of electric shock- Be careful to avoid bring electrocutes
WARNING SIGNS
Warning signs on laboratory chemicals and apparatus
Some
of the chemicals and apparatus used in biology laboratory may be
harmful or dangerous. Before starting using any chemical you must know
whether the chemical is toxic, flammable, oxidizing, explosive or
irritant/harmful. To help you recognize such dangerous substances, the
containers of modern chemicals carry special chemical warning signs as
indicated below.
1.Toxic
Toxic
substances can cause death. They may be poisonous when swallowed,
breathed in or absorbed through the skin. Examples of toxic substances
include acids and alkalis, lead II acetate and potassium dichromate.

2.Flammable
substances
are substances which can catch fire easily. Examples of such
substances include petrol, alcohol, Thomas Baker (Phosphorus yellow or
phosphorus red) and potassium metal. These substances normally evaporate
fast and therefore should not be brought near open flames.

3.Corrosive
Corrosive
substances attack and destroy living tissues. They may destroy the
floor, desks as well as metals, examples of corrosive substances are
concentrated acids, e.g. sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid
and concentrated alkalis e.g. sodium, potassium and ammonium hydroxides.
If by accident a corrosive substance comes into contact with your skin,
go to the sink and wash with a lot of water

4.Oxidant
An
oxidant is a chemical or substance which accelerates burning. Small
fires can be made big in the presence of oxidizing agent. Examples of
oxidizing agents include potassium permanganate, potassium chlorate, and
zinc nitrate.

5.Explosive
An explosion is a forceful rapid reaction which involves random throwing of particles

6.Harmful or irritant
Harmful
substances have a long term effect. They do not kill immediately. They
have a cumulative effect. Therefore careful handling is required.

Irritant
substances cause pains on the skin or eyes. They can endanger one's
health if they come into contact with the skin or eyes for too long.
Examples of harmful substances include lead chloride, lead nitrate, lime
water ferrous sulphate and manganese (IV) oxide
 |
8.Fragile-Can break easily
9.Radioactve substances- Give off harmful radiation which can cause damage to living tissues
10. Bioharzards are usually substances containing microbes or other factors which could cause disease
NOTE When working in the a biology laboratory we have to follow certain rules to ensures the safety of our selves and those around us.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS WHEN GIVING FIRST AID
 |
| Fig Fragile |
9.Radioactve substances- Give off harmful radiation which can cause damage to living tissues
10. Bioharzards are usually substances containing microbes or other factors which could cause disease
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS WHEN GIVING FIRST AID
First Aid is
given to the victims of:-Snake bites and stings from arthropod (like scorpion,
spider, bees, and wasps) and certain hairy
caterpillars.Shock.Fainting.Excessive vomiting.Strains, cramps and sprains of
muscles.Bone fractures and dislocations..Excessive bleeding, such From wound or
nose bleeding.Poisoning.Choking.Drowning.Dog bite.Burns.
Body substance
isolation, these are equipment and procedures that protect you from the blood
and body fluids of the patient. These include protective gloves, eye
protection, mask and gown. Snake bites.
1.. SNAKE BITE
1. Types of
snakes:Non-poisonous snakes include African green snake and African beauty
snake. These are of no danger to people. They rarely bite people, if they do
they have no poisonous fangs and they have no fang marks.
Poisonous snake
have fangs which are hollow like injection needles. They sink their fangs into
the victim and inject Venom (snake poison) through them. In many cases the
amount of poison is small and of no danger to life. 95% of persons survive
snake bites even without antivenin.
| Fig snake bite |
Types of snake bite poisoning Local poisoning causes pain and
swelling around the bite and no general poisoning of the whole body and
therefore no danger to life.
General poisoning affects the whole body. This occurs within half an hour or several days.
Cobra, the venom causes increasing weakness, difficulty to open eyelids and swallowing, eventually paralysis.
General poisoning affects the whole body. This occurs within half an hour or several days.
Cobra, the venom causes increasing weakness, difficulty to open eyelids and swallowing, eventually paralysis.
Viper, the
venom causes bleeding from the gums and fang marks with much pain and swelling
around the bitten part. Treatment of snake bites-Calm and reassure the
casualty and lay them down.-Stay quiet and do not move the bitten part. The
more it is moved the faster the poison will spread in the body.
TREATMENT OF SNAKE BITE
i.Calm the person and have them lie or sit down
ii Tightly or wrap a
wide elastic bandage or clean cloth around the limb above the bite to stop the
spread of venom in the blood stream.
iii.Keep the wound at heart level or lower in order to reduce the flow of venom to other parts of the body
iii.Remove all jewellery, for example bangles and tight clothing such as shoes and socks from injured limb
.iv. Wash the wound with soap and water to remove the venom.
-Do not apply ice orcut the wound or try to remove venom from the wound
v. If breathing stops start mouth to mouth respiration/ventilation
iii.Remove all jewellery, for example bangles and tight clothing such as shoes and socks from injured limb
.iv. Wash the wound with soap and water to remove the venom.
-Do not apply ice orcut the wound or try to remove venom from the wound
v. If breathing stops start mouth to mouth respiration/ventilation
-Never drink
alcohol after snake bite because it will increase heart rate and make poison to
spread rapidly to bloodstream
.vi.Take the
person immediately to hospital on a stretcher if possible. If possible carry
the snake with you, this will help the doctor to know which anti-snakebite
2. INSECT BITES AND STING
.Insect bites
are very painful but not dangerous except occasionally to children. Some biting
insects transmit diseases like malaria (mosquito anopheles) and sleeping
sickness (tsetse fly). A person bitten by such insects should seek immediate
medical help.
-Spider bites:
some spiders like black widow can cause extreme pain in stomach
muscles.-Scorpion, bee or wasp sting are very painful.
-Certain hairy caterpillars cause pain and local rashes.
-Certain hairy caterpillars cause pain and local rashes.
| Fig insects |
TREATMENT
i.Remove the sting by scrapping gently using a blunt object such as plastic card.
-Do not use your fingers or sharp object because this will make the sting to release more venom into the body
ii.Wash the stung area with soap and water
iii. Apply baking soda paste on the stung area(use ratio of 1 teaspoon of water to 3 teaspoon)The sting is acidic, baking soda is a base and so it neutralize the aid
iv.Apply a cold compression on the affected area to relieve pain and swelling.
-If the victim develops allergic reactions for example nausea,diarrhea, dizziness or swelling of the lips or throat take the person to the hospital immediately
3. EXCESSIVE BLEEDING FROM WOUND.
The principle
of controlling blood loss is to restrict the blood flow to the wound and
therefore encourage clotting. This can be done:
-By elevation
of the injured part if it is the limb or hand
.-By applying
pressure, i.e. Direct or indirect pressure.*Direct pressure is applied to the wound.
This flattens the blood vessels in the area and helps to slow the blood flow.
It can be by using ones hand or a clean piece of cloth.*Indirect pressure is
applying pressure to the artery that supplies blood to the affected area. This
is applied only in case of severe bleeding and should be applied for no longer
than 10 minutes
.-If the
bleeding cannot be controlled by pressure and elevation, tie a wide piece of
folded cloth or a belt tightly around the area above the wounded part.
Loosen
the tie after every hour to test whether the bleeding has stopped and to allow
blood to circulate. Take the casualty to hospital.
4. NOSE BLEEDING.
TREATMENTS
-Sit the
patient quietly with their head tipped forward.
-Blow the nose
gently to remove mucus and blood.
-Get them to
pinch their nose for 10 minutes and breathe through the mouth.
-Advise the
patient not to talk, swallow or sniff.-If the bleeding has not stopped after 10
minutes, repeat the process.
-If that does
not help, plug wet cotton in to the nose but leave a good part outside that it
can be easy to remove the plug.
-If a person
bleeds frequently, smear a little Vaseline inside the nose twice a day or sniff
lightly salted water.
-Eating fruits
like oranges, tomatoes, papaws and others is the best way to prevent nose
bleeding. 6. Shock.Shock is a sudden violent disturbance of the mind or
emotions.
5.ELECTRIC SHOCK.
Electric
shock includes redness, swelling, scorching or charring of the skin,
unconsciousness, stoppage of breathing.
TREATMENTS
-Turn off the
electricity immediately. If this is not possible, use dry wooden pole to remove
the casualty away.. Be very careful to avoid contact with the electric
current
-.Apply mouth
to mouth respiration/ventilation if necessary.If the casualty has visible burns
hold under cold running water for 10 minutes. Then apply sterile dressing
.-Do not apply
lotion, fat or ointment.
-Do not break
the blisters or remove any loose skin.
-If the person
complains of thirst, moisten the lips with water but do not give anything to
drink..Then follow the procedures of treating shock above.
6..FAINTING
It is caused by
sudden fall in blood pressure, which results, from inadequate blood supply to
the brain. The brain cells lack oxygen hence the victim collapses.
CAUSES
OF FAINTING.
-Bad news, eg.
death of loved onesUnpleasant sights, eg. snakeShockIllnessExcessive bleeding
TREATMENTS
-Loosen the
cloth, belt, shoes wristwatch and pants.Lay him/her down with the head lower
than the feet.
-Let him/her
have plenty of air, ie. Fan him/her.If the person is not breathing,
-Artificial
respiration (Resuscitation) or mouth to mouth respiration must be started at
once.If situation does not improve seek medical help.
7.VOMITING
Vomiting is
involuntary ejection of substances from the stomach through the mouth.
| Fig. Vomiting |
TREATMENT.
-Lay the patient
on his chest with head low, tilted back and to one side.
-Give nothing
by mouth except ice chips or repeated sips of cold, carbonated beverage.
-If vomiting
continuous give a redehydration drink (solution of 1 teaspoon of salt, 8
teaspoons of sugar and 1 litter of water)Allow the patient to have complete
rest.
-If vomiting
persists, take him/her to hospital, drugs like Promethazine Hydrochloride syrup
may be given.
8.
HICCUPS
Hiccups are
caused by an involuntary contraction of the respiratory muscles, giving a
characteristic sound.
May be due to
swallowing of air.
TREATMENT
.In children, a
teaspoonful of a weak solution of sodium bicarbonate or lemon juice.
-Application of
ice on the back of the neck.Holding the breath for as long as possible
-Swallowing
finely crushed ice
-.Pressing on
the eyeballs not too hard.
-Drinking a
glass of water upside down or while holding a pencil crossways between the
teeth.Pulling on the tongue
-Breathing with
paper bag held over your mouth.
9.MUSCLE CRAMPS.
Muscle cramps
are the result of a muscle going into uncontrolled spam and contraction causing
severe pain and restriction or loss of movement.
This can be due
to lactic acid during vigorous activities or lack of salts in the body.
TREATMENT.
-Keep the
sprained part raised high.Put ice wrapped in a cloth.Massage the cramped muscle
gently and apply some ointment like Deep heat or Volin.
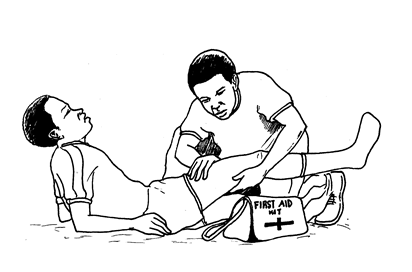

10.BONE
FRACTURE(broken bone).
Fracture is a
broken bone usually with an odd shape and painful swelling. If the bones are
far out of position and the break is recent, you can straighten them before
putting on a cast.
-Never force
setting of bones.Keep the broken bone in a fixed position by using a splint,
strips of bark or sleeve of cardboard.
-In case of
broken neck or back should not be moved by inexperienced helpers.At the health
centre they will put POP.
11.DISLOCATION.
These are bones
that have come out of place at a joint.
-Try to put the
bone back into its place.
-Keeping it
bandaged firmly in place so that it does not slip out again.Avoid forceful use
of the limb long enough for the joint to heal completely.
12. CHOKING.
Is when
something like food stuck in the throat, and the person fails to breath.
TREATMENTS.
 |
| Fig.Choking |
TREATMENTS.
-Stand behind
the person and wrap your arms around his waist.
-Put your fist
against his belly above the nave and below the ribs.Press into his/her belly
with a sudden strong upward jerk.
-:Lay him on
his back.Sit over him/her with the heel of your lower hand on his belly between
his navel ad ribs.
-Make a quick
strong upward push.Repeat several times if necessary.
-If still he
cannot breath try mouth to mouth respiration.
13. Drowning
A person who
has stopped breathing has only 4 minutes to live.
-Quick action
to save life must be taken.Start mouth to mouth at once before he is out of
water..
-When you reach
the shore, quickly put his head lower than the feet.
-While still
doing mouth to mouth, push his belly with an upward push to remove water out of
the body
14.WOUND
(Cuts, scrapes or abrasion and small wounds)
-Wash your
hands with clean boiled water and soap.
-Wash the
abrasion or wound gently with soap and clean boiled water and dry it.Add GV
(Gentian Violet solution to keep it clean and dry quickly.
-Do not close
the wound.
-Ensure that
the person is given tetanus injection.
- Deep and dirty wound.
-Wash your
hands with soap and clean water.
-Wash the wound
with clean cold water, be careful to clean all the dirt.Lift up and clean under
any flaps of skin.
-Put a clean
gauze to cover the wound.
-Change the
gauze every day. Take the person to the hospital for further medication and
tetanus injection.
NB.Never put
animal dung or human faeces or mud on the wound, these may cause dangerous
infections like tetanus.
16..BURNS
Types of
burns*1st degree burns are minor burns that do not form
blisters. Put the burned part in cold water at once and take painkillers.
2nd degree
burns are burns that form blisters.
Never break the
blisters. If broken wash gently with soap and cold boiled water. Leave the burn
uncovered and allow it to dry.
Apply GV to
keep it clean and speed up to dry. Covering the burn with honey helps heeling.
If the burn is near moving joint, sterilize a little Vaseline by heating it
until it boils and spread it on a piece of sterile gauze.
When it is cool
put the gauze on the burn.
*3rd degree burns are burns that destroy skin and expose raw or charred flesh and they cover large areas. Take the person to the hospital meanwhile wrap the burnt part with a very clean cloth or towel. Treat as 2nd degree burn.
*3rd degree burns are burns that destroy skin and expose raw or charred flesh and they cover large areas. Take the person to the hospital meanwhile wrap the burnt part with a very clean cloth or towel. Treat as 2nd degree burn.
17. EMERGENCY CAUSED BY HEAT..
Heat cramps
occurs as a result of depletion of salt in the body when working in hot weather
Sometimes a person sweats a lot and gets
painful cramps in the legs, arms or stomach.
TREATMENTS.
-Have the
person in a cool place and gently massage the painful areas. Put a teaspoonful
of salt in a litre of boiled cold water, stir and drink.
- Heat
exhaustion, a person who works and sweats a lot in hot weather may become very
pale, weak and feel faint. The skin is cool and moist.
The pulse is
rapid and
TREATMENT
-Have a
person lie down in a cool place
. -Raise
his feet and rub his legs
. Give salt
solution to drink. Heat stroke, Occurs in old people or alcoholics during
hot weather. The skin is very hot and dry.
-Not even the
armpits are moist. High fever up to 42 0C. Person is often
unconscious.
- Put him in the shade. Soak him with cold water or ice water and fan
him. Continue until the fever drops. Then seek medical help