CELL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION.
THE CELL
The cell is a structural and functional basic
unit of life.
Cells are small microscopic units that make up the bodies
of all living organisms.
The cell is fundamental to Biology as the atom is to
Chemistry. The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live.
Plants
and animals are made up of units called cells. The cells are
microscopic in such a way that they cannot be seen by our naked eyes.
Some organisms like protozoa, diatoms and bacteria consist of one cell
and are called single-celled or unicellular organisms. Some are made up
of many cells and are called multicellular organisms.
Therefore a cell can be defined as the smallest unit of living things or a cell is a basic unit of life.
History of the cell.
In 1665, Robert Hooke discovered the structural and
functional unit of all living organisms called the cell.
In 1839, Schleiden J.M. and Theodore Schwann, put
forward the cell theory, which states that, “Cells are of universal occurrence
and the fundamental units of an organism”.
The
cell structure of living things was first seen by Robert Hooke in 1667
when he examined fine slices of cork. Robert Hooke believed that the
cells were empty and that the cell wall and cell membrane were the most
important parts of the cell but now cell contents are seen to be the
most important ones.
The Characteristics
Characteristics of the cell include the following:
- Cells are small microscopic structures which cannot be seen by our naked eyes.
- Cells are capable of dividing by mitotic process or meiotic process.
- Cells contain structures called organelles.
The cell theory
The cell theory state that
- All living things are composed of cells.
- Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living things
- All cells are produced from other cells
- cells contain inherited information which controls their activities
- All cells are basically the same in chemical composition
- all life processes take place in the cell
Unicellular and multicelular.
Unicellular are organism that are made up of only one
cell, eg. Bacteria, amoeba, and paramecium.
TYPES OF THE CELL
There are two types. namely
PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS
Prokaryotic cells
are cells with no membrane-bound nucleus. The DNA lies free in the
cytoplasm in a region known as nucleoid. They have no true nuclei.
Examples of prokaryotic organisms are bacteria.
Eukaryotic cells
are
cells whose nuclei are bounded by nuclear membrane. They are surrounded
by two nuclear membranes called nuclear envelope. Examples of
eukaryotic organisms are protoctists, fungi, plants and animal cells.
Characteristics of a cell.
· Is microscopic
· Is membrane bound
· It has structures that are sites of
chemical reactions called organelles
· Have the ability to replicate since it
contains the genetic material, i.e. DNA and RNA.
Different between prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
| Eukaryotic cells | Prokaryotic cell |
| They have nuclear membrane | Lack nuclear membrane |
| Organelles are surrounded by envelopes Have true nucleus | Organelles are not surrounded by envelopes |
| Have no true nucleus |
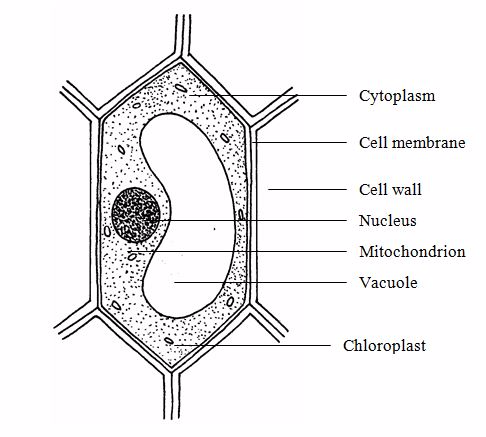
The Functions of Different Parts of Plant and Animal Cells
Basically a cell has three main parts
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
Cell membrane (plasmalemma)
This is a thin flexible membrane made of protein and oil. It has the following functions:
- The cell membrane encloses the contents of the cell.
- It is freely permeable to water and gases only and selectively permeable to other molecules e.g. it allows food in but keeps unwanted molecules out. Thus cell the membrane controls the substances entering and leaving the cell
|
Cell wall
|
Cell membrane
|
|
It is a non–living structure
|
It is a living structure
|
|
It is made up of cellulose
|
It is made up of lipoprotein
|
|
It is freely permeable
|
It is selectively permeable
|
2..Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
is a transparent jelly-like fluid and may contain particles such
chloroplasts or starch grains or oil droplets. It contains up to 80%
water and the remainder is mainly protein. It is a place where chemical
reactions take place
3.Nucleus
A
nucleus is a ball-shaped or oval body located inside the cytoplasm. It
cannot usually be seen unless the cell has been stained with certain
dyes. It consists of nucleoplasm bounded by nuclear membrane. The
nucleus is a cell control centre.
The functions of the nucleus:
- It controls the formation and development of a cell.
- The nucleus also controls chemicals which the cell manufactures.
- The nucleus contain chromosomes which carry genetic material i.e. DNA which is responsible for controlling genetic information.
4.Cell wall
The
cell wall is only found in plant cells. It is made up of cellulose.
When the cell is growing the cell wall is fairy plastic and extensible.
It becomes tough and resists stretching when the cell has reached full
size. The cell wall is non-living.
functions:
1.It gives the cell its shape.
2. It is freely permeable to all kinds of molecules.
3.It supports and protects the cell.
4.It supports non-woody plant organs, such as leaves, by turgor pressure.
5.It osmoregulates by resisting entry of excess water into cell.
5.Vacuole
In
animal cells, vacuoles are small droplets of fluid in the cytoplasm
variable in size and position. In plant cells, the vacuole is a large,
permanent fluid-filled cavity which occupies a greater part of the cell.
In plants, the fluid is called cell sap. The cell sap may contain salts, sugar and pigments dissolved in water
functions:
- It is responsible for food storage and osmoregulation.
- The outward pressure of the vacuole on the cell wall makes the plant cells firm, giving strength and resilience to the tissues.
6.Mitochondria
Mitochondria
are found in all aerobic eukaryotic cells.
A mitochondrion is
surrounded by an envelope of two membranes, the inner being folded to
form cristae (singular: crista).
It contains a matrix with a few ribosomes, a circular DNA molecule and phosphate granules.
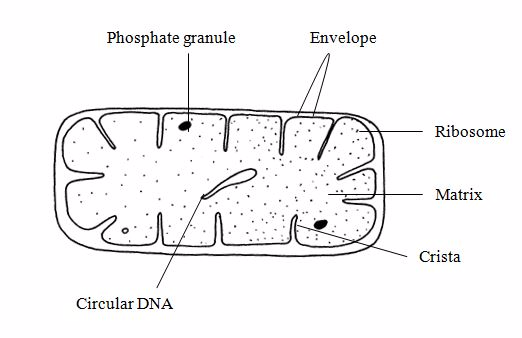
Functions of mitochondria.
-Are the sites or respiratory reaction, which
yield energy for the cell
7.Chloroplast
Chloroplasts
are disc-shaped organelles.
They are found in plant cells and algae
cells. A chloroplast contains a green substance called chlorophyll. It
is surrounded by an envelope of two membranes and contains gel-like
stroma through which runs a system of membranes that are stacked in
places to form grana.
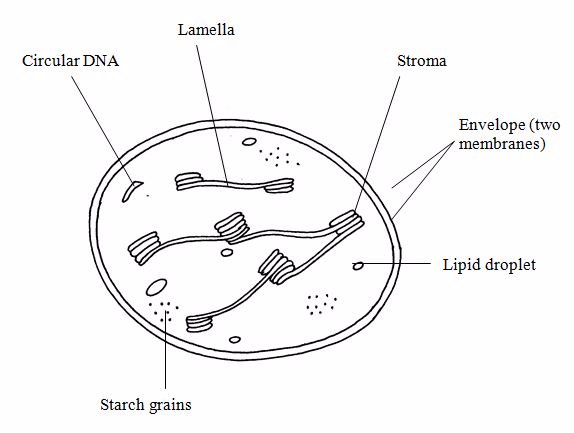
Functions of chloroplast.
They are the sites of photosynthesis, ie. The process
by which green plants manufacture carbohydrates.
-The reaction
of light stage of photosynthesis take place in the grana.
-The
reaction of the dark stage of photosynthesis take place in the stroma of the
chloroplast
Golgi body
Golgi bodies are stacks of flattened, membrane-bound sacs
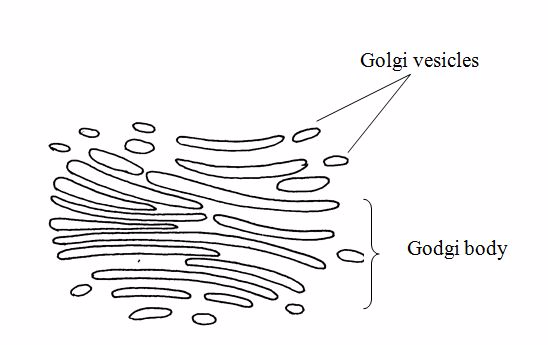
The functions:
- Golgi bodies are responsible for internal processing and transport system.
- Processing of many cell materials e.g. protein takes place in the cisternae.
- Godgi vesicles transport the materials to the other parts of the cell
PLANTS AND ANIMAL CELLS
Animal cell
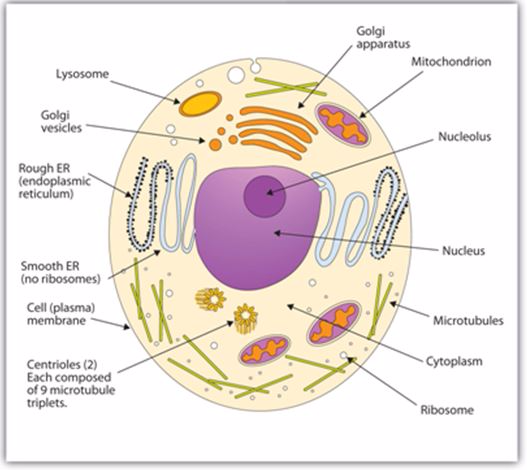
Plant cell
Differences between plant cell and animal cells
Animal cell
|
Plant cell
|
Have no cell wall
|
Have cell wall made of cellulose
|
Have small temporary vacuole
|
Have large permanent vacuole
|
Ho no chloroplasts
|
Have chloroplasts
|
Hove no definite shape
|
Have definite shape
|
Have centrioles and normally exist in pairs
|
They usually lack centrioles.
|
They store fats and glycogen.
|
They store oils, proteins and starch.
|
The cytoplasm occupies most of the cell with the
nucleus centrally located in the cytoplasm.
|
The cytoplasm and the nucleus are located towards
the periphery.
|
They are usually smaller.
|
They are normally larger.
|
Similarities between animal cell and plant cells
- Both have cell membranes
- Both contain cytoplasm
- Both have nucleus
- Both have mitochondria
- Both have golgi bodies
- Both have ribosomes
CELL DIFFERENTIATION CELL
An organism made up of one cell is called unicellular organism. Example. are a Amoeba. paramecia and bacteria and
An organism made up of more than one cell are called Multicelllrar organism.A multicellular organism consists millions of cells
CELL DIFFERENTIATION
is the way cells adapted so that they can carry out function efficiently.
or
The process by which cells are specialized to perform a particular function
These involves the
changes in shape and chemical reactions enable the cell to carry out
its special function. is called cell differentiation or ‘division of labour’
within the organism. Similarly, the special functions of mitochondria,
ribosomes and other cell organelles may be termed as division of labour
within the cell.
TISSUE.
is formed when a group of cells that perform the same function.. Examples.animal tissue. are bone, muscle, and skin.
Plant tissue. Xylem and Phloem.Animal organ includes Hearts,Liver, and brain
and Plant organs includes the stem, flowers, and roots.
A SYSTEM.
is made up of organs that work together to perform a certain functions..Examples
are respiratory system, digestive system . reproductive system, Hormonal system skeletal system and blood circulatory system.
AN ORGANISM
Is made up of different system working together.
Therefore there is special organization from the
Cell----tissue-----organ-----system------organism
THE IMPORTANCE OF CELL DIFFERENTIATION.
Leads to division of labour. Means each cell does a specific function.
This help the body to carry out all life processes at the same time and more efficently, organs and body systems
.
SPECIALIZES ANIMAL CELLS.
ANIMAL CELL
1. Nerve cells
These
are specialized for conducting impulses of an electrical nature along
the fibre. The fibre may be very long e.g. from the foot to the spinal
column. They are the longest cells known.
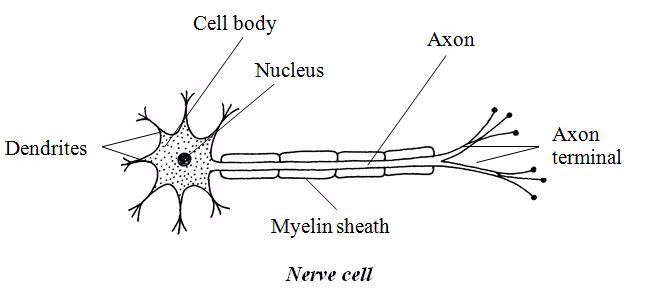
Nerve cell
2.BLOOD CELL
- White blood cells: These cells occur in blood stream and are specialized for engulfing harmful bacteria. They are able to change their shapes and move about, even through the walls of blood vessels into the surrounding tissue.
White blood cell
- Red blood cells. These cells are responsible for transportation of oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body.
Red blood cells
- Platelet cells: Platelet cells are found in the blood. They are also called blood platelets. Their function is to help clot the blood at wounds and so stop bleeding.
Reproductive cells
- Sperm cell: it is a male gamete produced in the testes.
Sperm cell
- Egg cell:It is a female gamete produced in the ovary.
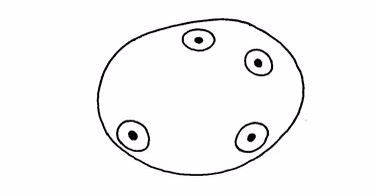
Egg cell
4.Muscle cells
These
are elongated cells which form the muscle tissues. Muscle cells are
highly specialized in that they are able to shorten a half or even a
third of their resting lengths. This characteristic enables the muscles
to contract and expand.
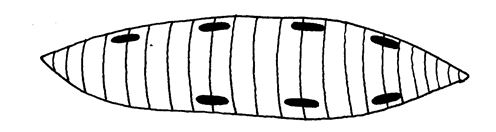
Muscle cell
5 Ciliated cells
These cells form the lining of the nose and wind pipe.
PLANT CELL
1.Root hair cells
These
cells form the outer layer of young roots. The cells are specialized to
absorb water and mineral slats from the soil. The hair-like projections
penetrate the soil particles and offer a large absorbing surface.
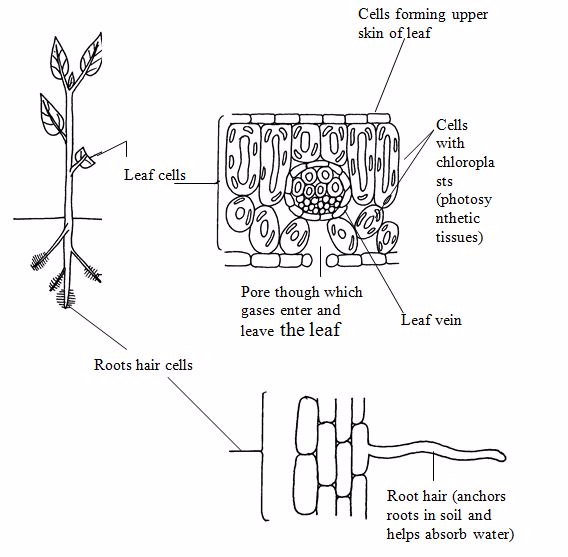
2.Phloem cells
These
are food conducting cells in a plant, joined end to end, and where they
meet, perforations occur in the walls. Through these holes, the
cytoplasm of one cell communicates with the next.
Xylem cells
The
cells conduct water and mineral salts form the soil to all parts of the
plant. They are also responsible for mechanical support.
- Parenchyma cells
- Collenchyma cells
- Sclerenchyma cells
- Epidermal cells
TISSUES
A tissue is a group or collection of similar cells performing a specific function. Tissues vary in size, shape and function.
Examples of tissues
ANIMAL TISSUE
Animal tissues include epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, nervous tissue, blood tissue and bony tissue.
Epithelial tissue:
Epithelial
tissues cover the body lining cavities, hollow organs and tubes. They
are responsible for(i) protection of the underlying structure from
dehydration, and chemical and mechanical damages;(ii) secretion;
and(iii) absorption.
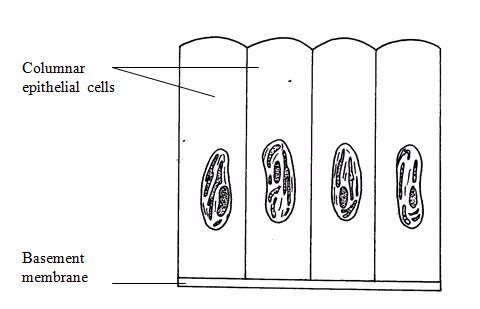
Columnar epithelium
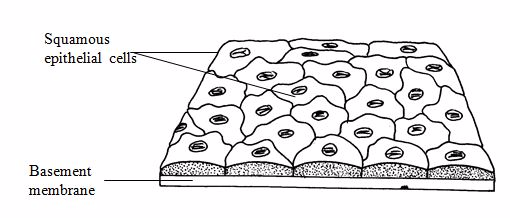
Squamous epithelium
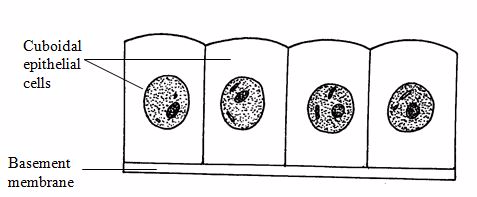
Cuboidal epithelium
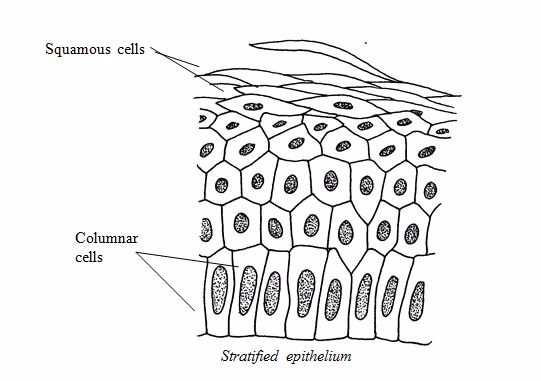
Stratified epithelium
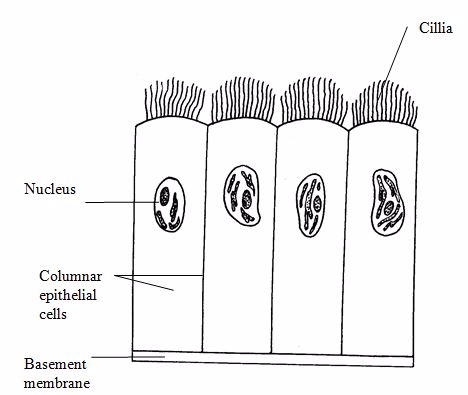
Cliated columnar
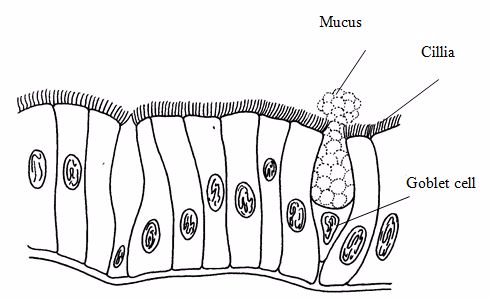
Cilliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
Muscle tissue
Muscle tissue consists of cells specialized to contract and move the body. Muscle tissues can be:
- skeletal muscle tissue;
- smooth muscle tissue; or
- cardiac muscle tissue.
1Skeletal muscle tissues form those muscles that move the bones
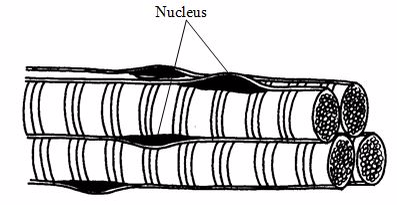
Skeletal muscle fibres
2.Smooth muscle tissues
These are found in the walls of hollow organs. They perform the following functions:
- Regulate the diameter of blood vessels and parts of the respiratory tract.
- Propel the contents of the ureters, ducts of glands and alimentary tract.
- Expel contents of the urinary bladder and uterus.
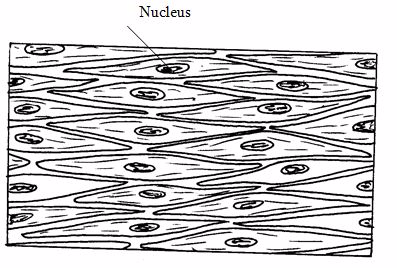
Smooth muscle fibres
3.Cardiac muscle tissue
This
kind of muscle tissue is found only in the heart wall. It helps in
contracting and relaxing of heart muscles thus pumping the blood to
various body parts.

Cardiac muscle fibres
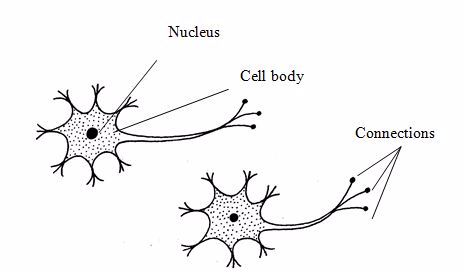
Nervous tissues
Nervous
tissues have endings that detect changes in the environment. They
transmit and conduct nerve impulses to the brain and spinal cord and to
the effector organs.
PLANT TISSUE
Examples
of plant tissues are collenchyma tissue, sclerenchyma tissue, epidermal
tissue, conducting tissues e.g. phloem and xylem, palisade tissue and
spongy tissue.
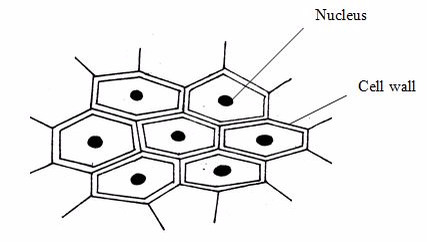
An onion epidermal tissue
ORGANS
An organ is a collection of tissues working together to perform a certain function
Animal organs
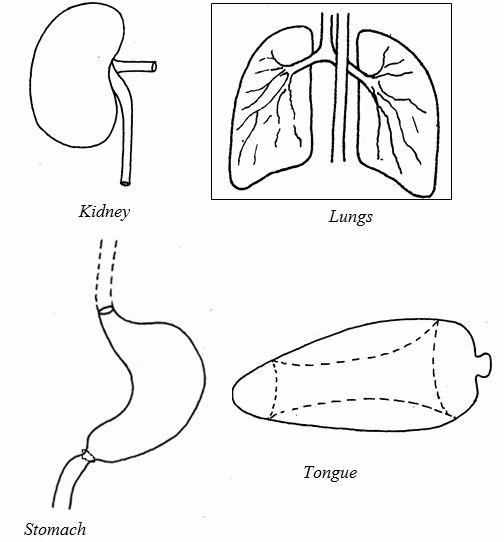
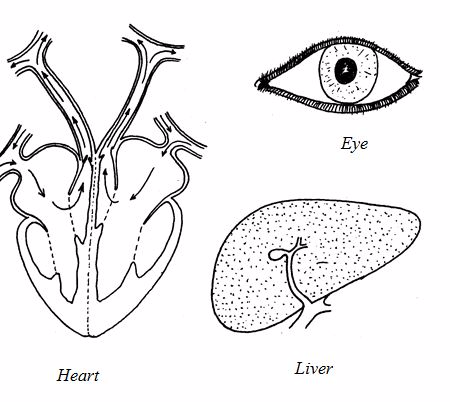
Other examples of animal organs include skin, testes, ears, noses and the brain.
Plant organs
Examples of plant organs include leaves, stems, roots, flowers and fruits.
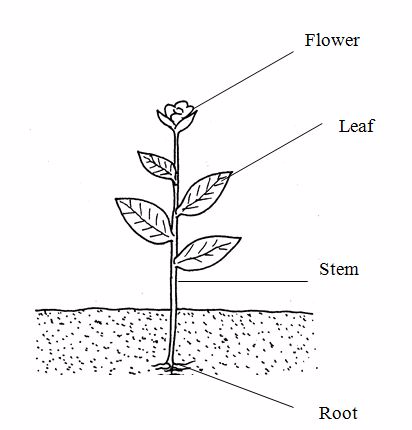
Plant organs
ORGAN SYSTEM
A system refers to several inter-related organs performing a particular function.
Digestive system
The
main organs that make up the digestive system are alimentary canal,
liver and pancreas.The main function of this system is to digest and
absorb food.
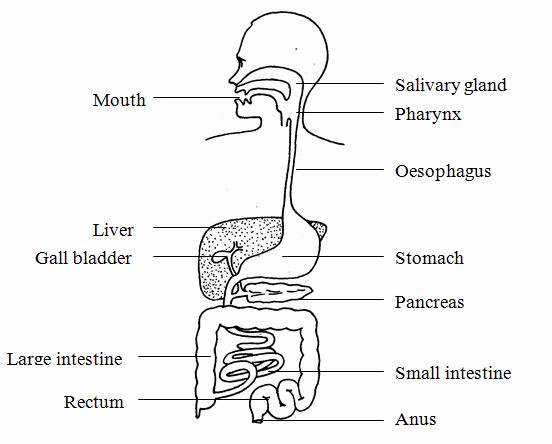
The digestive system
Circulatory system
This
system consists of the heart, arteries and veins.The role of the
circulatory system is to transport gases, food, hormones and distribute
heat.
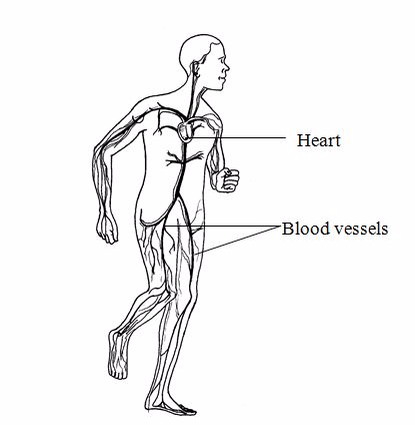
The circulatory system
Lymphatic system
Lymphatic
system has comprises of the lymph vessels and lymph nodes. The main
function of the lymphatic system is to transport materials and protect
against.
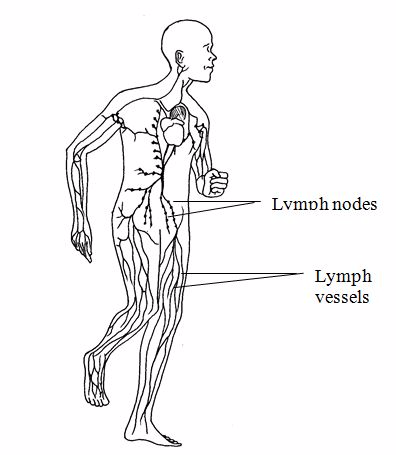
Lymphatic system
Respiratory system
The
respiratory system consists of the trachea and the lungs. The role of
the respiratory system is to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide
gas.
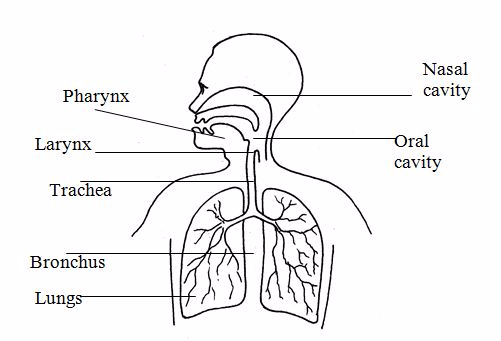
The respiratory system
The urinary system
The
main organs of the urinary system are kidneys, ureter, bladder and
urethra.The urinary system plays a role in removing metabolic waste
products from the body and also it is responsible for osmoregulation.

The urinary system
The nervous system
This system consists of the brain, spinal cord and nerves.The role of the nervous system is to detect and respond to stimuli.
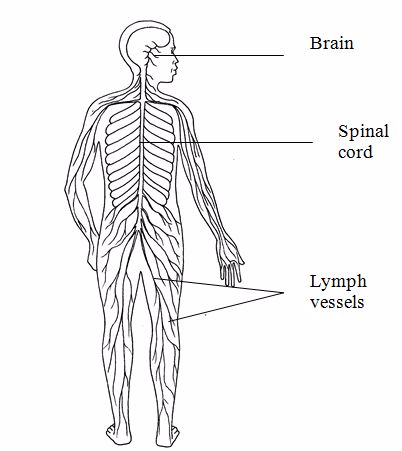
Muscular system
The muscular system
It consists of the organs muscles and tendons. The role of the muscular system is to bring about movement.
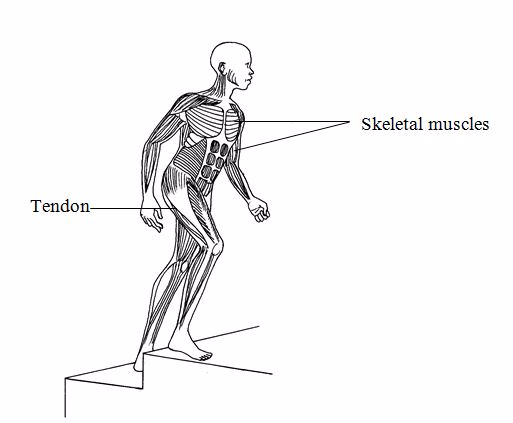
The skeletal muscles
The reproductive system
It consists of the ovaries, testes and uterus. Its role is to produce offspring.

Male reproductive system
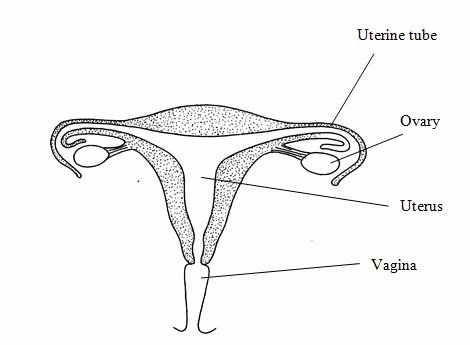
Female reproductive system
Endocrine system
It consists of endocrine glands. Its role is to produce hormones.
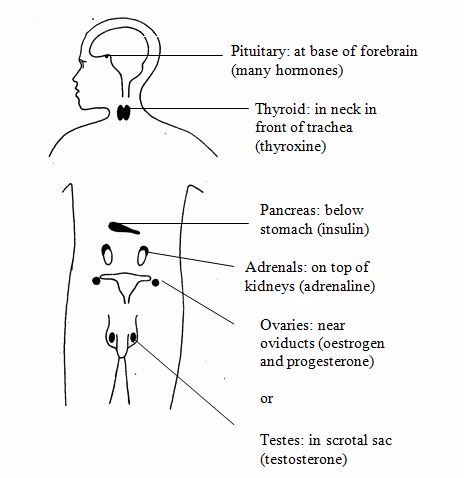
Endocrine system
Skeletal system
It consists of a system of skeletons. Its function is to support the body, protect internal organs and produce blood cells.

Skeletal system
Examples of organ system in plants
Root system –consists of roots
Function:
- Holds the plant firmly into the soil
- Absorption of water and mineral salts from the soil
- Sometimes they act as storage organs in some plants
Shoot system – consists of the organs flowers, fruits, stem and leaves
Function
- Site of reproduction
- Transport of substances
- Photosynthesis occurs in the shoot
- Transpiration processes.
