CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING
THINGS
Classification is the grouping of organism based on their similarities and differences.
The system of sorting out and placing organisms into different groups on the basis of their similarities and differences is called classification.
Organism that are similar are placed in the same group.
In the world, there are numerous
varieties of living organisms.These organisms do vary in size, structure,
shape, habitat, mode of feeding and even mode of reproduction. The organisms can
be sorted out and placed into different groups based on their similarities.
Biologists have designed a system that involves three main features.
1.The system is hierarchical.This means that a large classification group can be subdivided into smaller group or taxa.
2.Important,significant,biological similarities and differences are used to decide which group and organism goes on.Example whether organism is edible or non edible, Has backbone or not,are useful, significant biological differences
3.Every organism is given a name which tells you which group to belong.
1.The system is hierarchical.This means that a large classification group can be subdivided into smaller group or taxa.
2.Important,significant,biological similarities and differences are used to decide which group and organism goes on.Example whether organism is edible or non edible, Has backbone or not,are useful, significant biological differences
3.Every organism is given a name which tells you which group to belong.
The field of Biology that deals with classifying organism is called Taxonomy
ii.Classification makes communication easy among
biologists from different parts of the world
iii.It provides good organized system in which a newly
identified organism can be easily fitted in future.
iv.It makes it easier to identify organisms
v.It can be used to make assumption or prediction characteristics that are present in the members of the same group.
vi.Provides supportive evidence for evolution.
CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM
v.It can be used to make assumption or prediction characteristics that are present in the members of the same group.
vi.Provides supportive evidence for evolution.
CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM
There are are two types of biological classification system. Namely
1.Artificial classification
2.Natural classification
ARTIFICIAL CLASSIFICATION
An artificial classification is based on one or a few easily observable features. It usually designed for practical purpose with an emphasis on convenience and simplicity. In this type of classification, unrelated organisms are often placed in the same group while closely related organisms are often placed in different groups
ARTIFICIAL CLASSIFICATION
An artificial classification is based on one or a few easily observable features. It usually designed for practical purpose with an emphasis on convenience and simplicity. In this type of classification, unrelated organisms are often placed in the same group while closely related organisms are often placed in different groups
Example. Bats and birds would be placed in the same group because all have the
ability to fly since they posses wings. But apart from those two common, features bat and birds show several biologically significant difference.Bat has hair,mammary gland,sweat gland and different types of teeth theses distinguish bat as mammals,birds have beak ,lay shelled eggs hence not placed into mammal
In the third century B.C Aristotle used artificial classification to classify plants. He grouped plants according to their shapes and size and whether their were useful to man or not.
This types is known as dichotomous key
This types is known as dichotomous key
Advantage of artificial classification
1.It is easy to classify organisms since it is based on
few observable characteristics.
2. It does not take much time to classify organisms based
on this system (not time consuming).
3.It does not need expertise (even a layman can do).
4.It is relatively stable i.e. not easily changing from
time to time.
Disadvantage artificial classification
1.It tends to place closely related organisms into
different groups instead of being grouped together e.g. a bat can be
placed in a group of birds instead of mammals.
2..Different or unrelated organisms may be placed in the
same group e.g. bats placed in a group of birds, worms placed with snakes
in the same group
3 The system does not provide enough information about
its members.
4.It is difficult to incorporate additional information.
2.Natural classification
Natural system of classification
Natural system of classification
This groups organism according to both external and internal features
or
This type of classification system tries to use natural relationships between organisms.
It considers many features in common including internal as well as external features.
It considers many features in common including internal as well as external features.
Similarity of embryology, morphology,
anatomy, biochemistry cell, structure and behaviour are all considered relevant.
It is based on evolutionary relationship in which organisms belonging to the same
group are believed to have a common ancestor.
Organisms are placed in their natural group by using the following criteria
Characteristic features
which show homology are distinguished from those which show analogy. Example the
fore limbs of mammals, whales, birds and bats have the same basic pattern and
similar bone arrangement, i.e. homologous. This suggest s that these organisms
are coming from the same ancestor and that can be placed in the same group Organisms are placed in their natural group by using the following criteria
- Relations based on homologous (similarity in term of origin and structure ,but difference in functions E.g Forelimb of animals)characters not Analogous character((similarity in term of function, but no necessarily e.g. Wing of wings and grasshopper)
- Organism with many features in common
Advantages of natural
system of classification
i.Closely related organisms are placed in the same group.
ii.It reflects evolutionary relationships.
iii.Unrelated organisms cannot be placed in the same group.
iv.It makes it easy to incorporate additional information.
i.Closely related organisms are placed in the same group.
ii.It reflects evolutionary relationships.
iii.Unrelated organisms cannot be placed in the same group.
iv.It makes it easy to incorporate additional information.
Disadvantages of natural
system of classification.
a.It is difficult since it considers many features.
b.It requires expertise i.e. more knowledge about an organism.
c.It is time consuming.
d.It is relatively unstable i.e. it changes from time to time.
e.It is more expensive since more data are required.
a.It is difficult since it considers many features.
b.It requires expertise i.e. more knowledge about an organism.
c.It is time consuming.
d.It is relatively unstable i.e. it changes from time to time.
e.It is more expensive since more data are required.
Differences between
natural classification and artificial classification
MAJOR GROUP OF LIVING THINGS
Artificial classification
|
Natural classification
|
(i) Based on external features
only
|
Consider both external and
internal features
|
(ii) Does not reflect on
evolutionary relationships
|
Reflects on evolutionary
relationships
|
(iii) Requires simple skills
|
Requires advanced scientific
skills
|
(iv) It is usually fast and
inexpensive
|
Take more time and it is costly
|
(v) Less accurate
|
More accurate
|
(vi) New information cannot be
added
|
New information can be added.
|
MAJOR GROUP OF LIVING THINGS
The major groups of
living things are the kingdoms. Previously, living things were categorized into
two main groups; plantae and animalia kingdom. But this classification caused
difficulties since some organisms seemed to posses some of the
characteristics of both groups.
For example, euglena is capable of feeding like
an animal and locomote like an animal. Therefore, it is placed in animalia
kingdom. But the same euglena has chlorophyll and it is capable of
manufacturing its own food. Therefore, it should also be placed in plantae
kingdom. Such an organism does not seem to fit exactly in animalia or plantae
kingdom. Thus, euglenas are assigned in the major group of their own.
Currently, in Biology organism are classified into five
major groups (kingdoms) of living things
Ranks of classification or Taxa
The ranks of classification are
Kingdom
Phylum/division
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
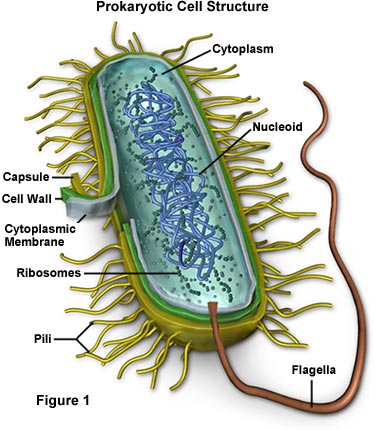
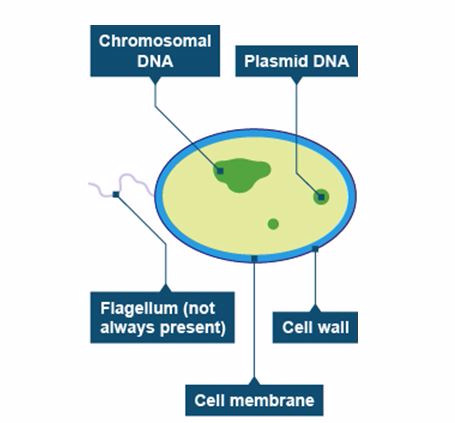
i..Kingdom monera. Foe example Bacteria
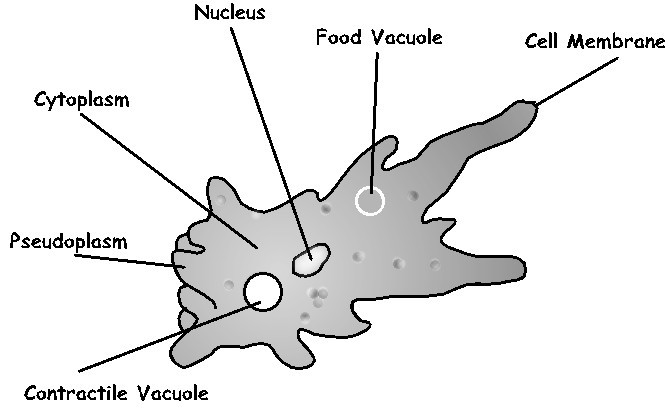
ii..Kingdom protoctista. For example amoeba
iii Kingdom fungi. For example mushroom
iv..Kingdom plantae For example maize
v..Kingdom animalia. For example Human being
Kingdom are subdivided into smaller units.
Kingdom Animalia is subdivided in Phyla (phylum singular) Kingdom plantae subdivided into division.
1.Kingdom-
this is the highest rank (taxon). It comprises of several related taxa. It
comprises of many organisms than any other taxon.
2.Phylum/division– this
is the second largest rank of classification. It consists of several
closely related classes.
3. Class -
members or this group have more characteristics in common than do members
of division or phylum.
4.Order-
it consists of groups that are more alike than those in a class.
5.Family –this
is made up of groups that are more alike than those in the order. Wolves
and cats are both in the order Carnivore but wolves are
in the family Canidae while cats belong to the
family Felidae.
6.Genus –
it consists of very similar species but members of different species
cannot breed one another.
7 Species – is a group of closely related organisms which are
capable of interbreeding and produce fertile (viable)offspring.
NB.Organism from difference species can interbreed and produce offspring..Normally the offspring is infertile.Examples
i.Mule-Mate between male donkey and female horse
ii.Geep - Matebetween a male goat and female sheep
iii.Zeedonk- Mate between femaleZebra and male donkey
iv.Ligers- Mate between male lion and female tigior
Binomial nomenclature
- Must have many features in common.
- Must be able to breed one another to produce fertile offspring.
- Must be distinct and different from other organisms.
Human being
|
Dog
|
Maize plant
|
|
Kingdom
|
Animalia
|
Animalia
|
Plantae
|
Phylum/Division
|
Chordata
|
Chordata
|
Spermatophyta
|
Class
|
Mammalia
|
Mamalia
|
Angiospermae
|
Order
|
Primate
|
Canivore
|
Graminales
|
Family
|
Hominidae
|
Canidae
|
Graminaceae
|
Genus
|
Homo
|
Canis
|
Zea
|
Species
|
spiens
|
familaris
|
May
|
Scientific name
|
Homo sapiens
|
Canis familaris
|
Zea mays
|
NB.Organism from difference species can interbreed and produce offspring..Normally the offspring is infertile.Examples
i.Mule-Mate between male donkey and female horse
ii.Geep - Matebetween a male goat and female sheep
iii.Zeedonk- Mate between femaleZebra and male donkey
iv.Ligers- Mate between male lion and female tigior
Binomial nomenclature
Binomial nomenclature is a scientific system of naming organisms where by name is made up of two latin words
The scientific process
of naming organisms is called nomen- clature. Biological nomenclature is based
on the binomial system (double naming system) pioneered by the work of a
Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778).
Biologists assign
scientific names to organisms so as to avoid confusion among themselves since
scientists from different countries use different languages. The scientific names
are uniform in all languages.
Rules of binomial
nomenclature
Scientific names of organisms must be in Latin language and if the names are derived from other languages, they must be latinized.
Scientific names of organisms must be in Latin language and if the names are derived from other languages, they must be latinized.
- A scientific name of an organism has two parts, genus
name and species name.
- A genus name always starts with a capital letter and a
species name follows with a small letter.
- In typed scripts, a scientific name must be written
in italics or underlined if hand written.
- A specific name is sometimes accompanied with the name
of the author who first described and named the organism.
- When an organism is known by several names, the valid name is the one which was established after the work of Linnaeus.
Examples of scientific
names
Human being:Homo
sapiens
Homo is the generic name and sapiens is
the specific name.
Other examples of
organisms with their scientific names
Common
name
|
Scientific
name
|
Earthworm
|
Lumbricus terrestris
|
Cockroach
|
Periplaneta
americana
|
Amoeba
|
Amoeba proteus
|
Coffee
|
Coffea
arabica
|
Maize
|
Zea mays
|
Bean
|
Phaseous
vulgaris
|
Domestic Cat
|
Feris catus
|
Sisal
|
Agave sisalana
|
Mango
tree
|
Mangifera indica
|
Coconut palm
|
Cocos
nucifera
|
Lion
|
Panthera
leo
|
Housefly
|
Musca
domestica
|
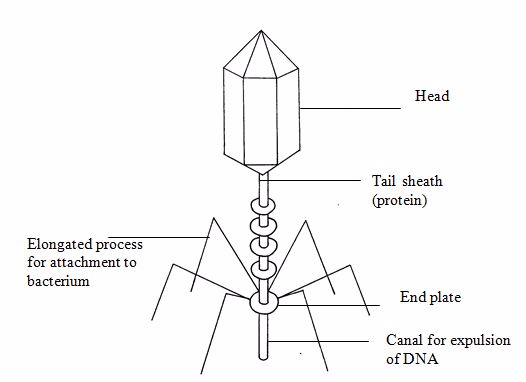
VIRUSES, KINGDOM MONERA and KINGDOM PROTOCTISTA
1.Viruses